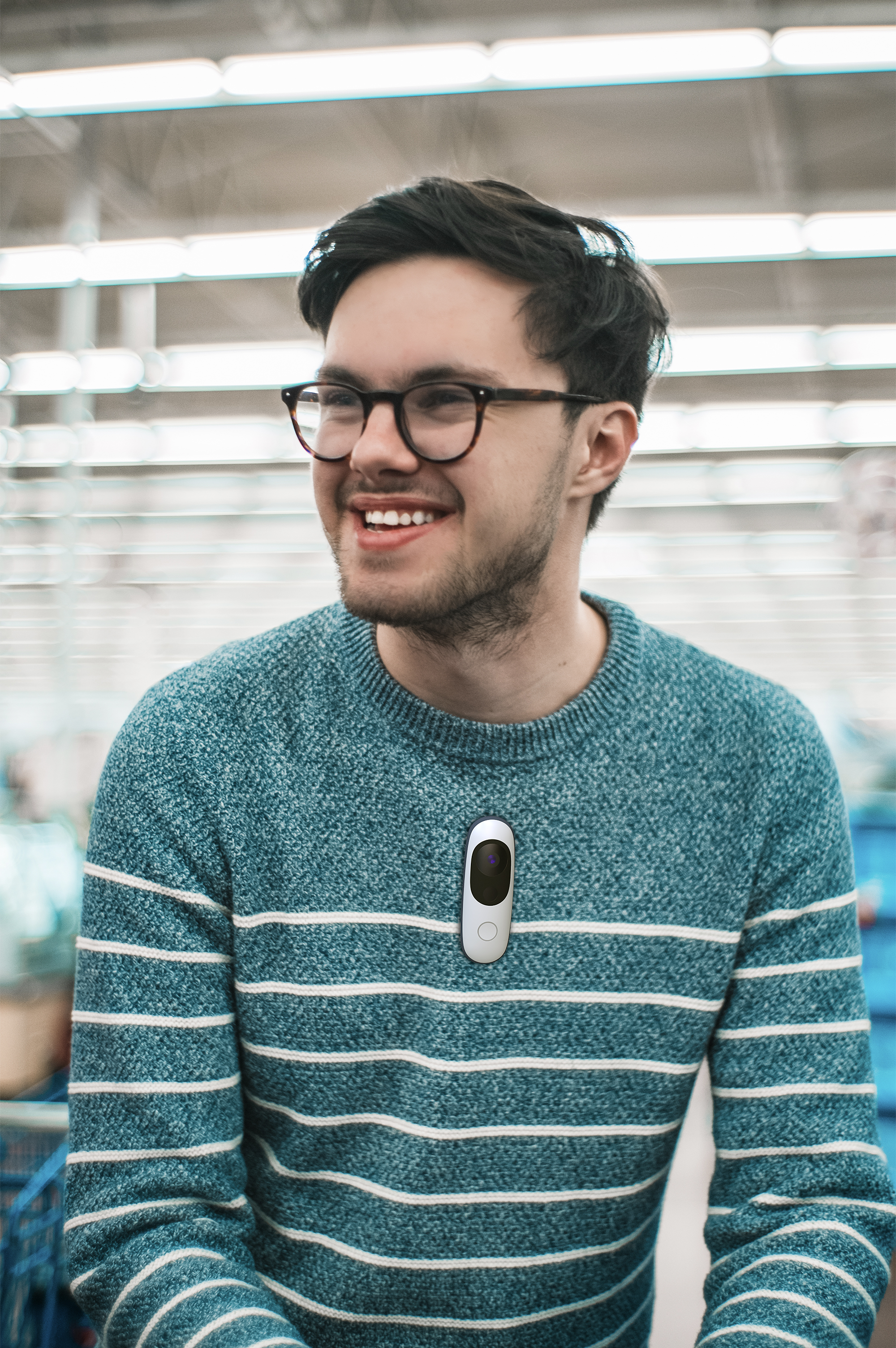
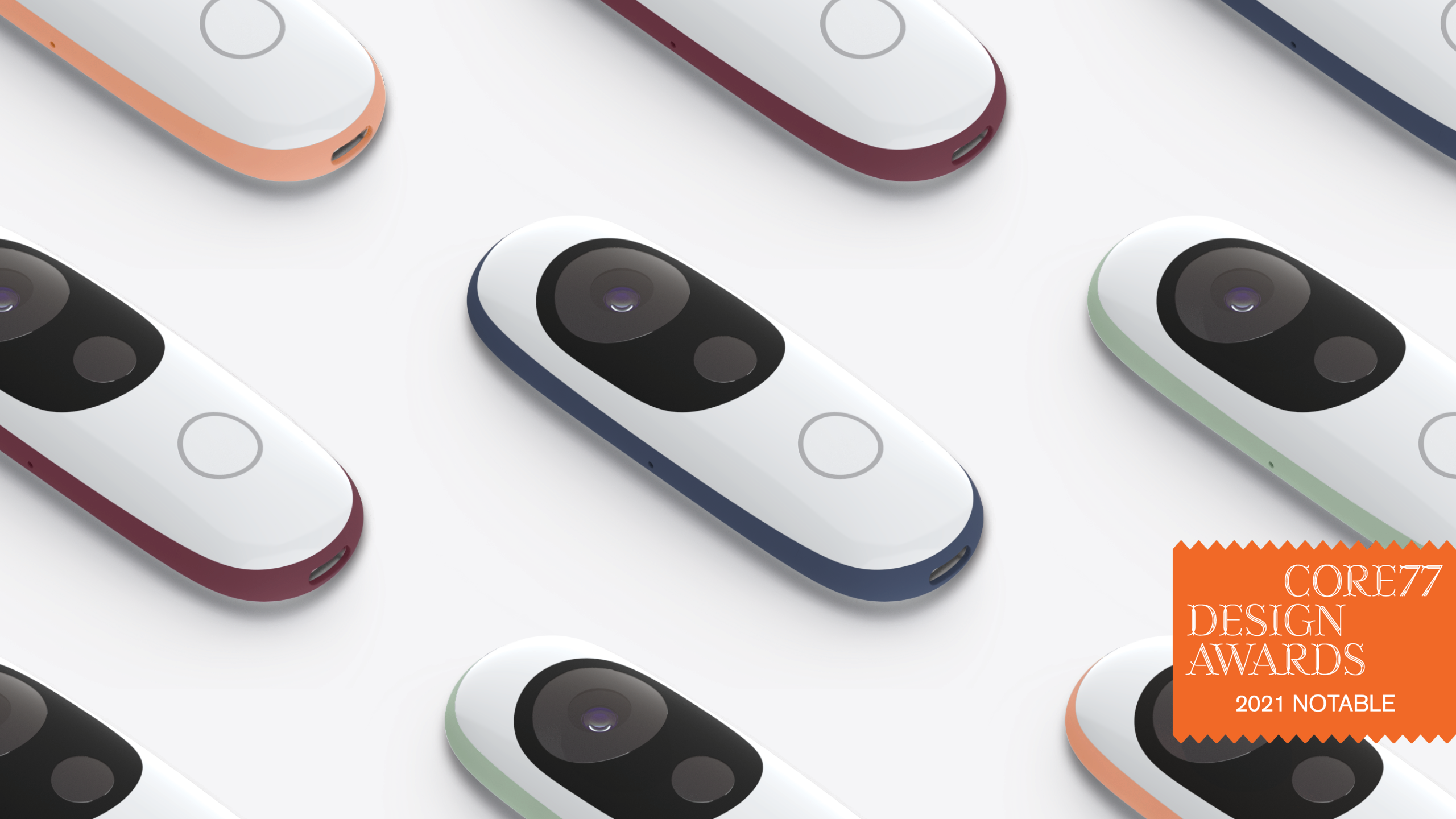
Iris is a comprehensive rehabilitation monitoring system made for blindness and low-vision (BLV).
We worked closely with vision occupational therapists (OT) to develop routines that help patients re-acquire essential daily skills. The wearable Iris tracker logs patients’ sessions at home so that they can continue developing the techniques learned from their OT appointments.
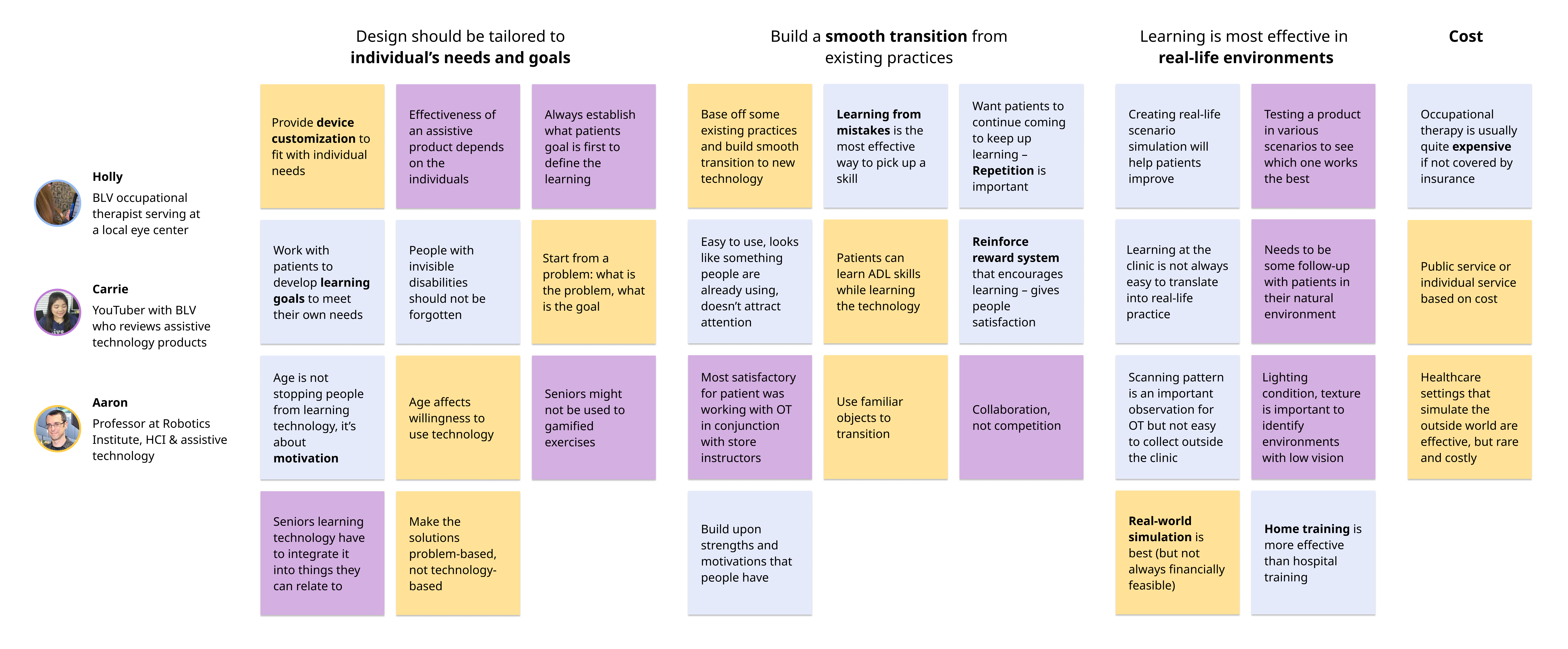
By bringing therapists and patients into each stage of the design process and building on existing therapy paradigms, the Iris system creates a positive reinforcement cycle for BLV therapy.
Roles
Industrial design
UX
User research
Sound design
Video production
Industrial design
UX
User research
Sound design
Video production
Team
Meijie Hu – digital UI, UX, user research, video production
Course
Design Research Studio
Duration
September – December 2020
Meijie Hu – digital UI, UX, user research, video production
Course
Design Research Studio
Duration
September – December 2020

Our research revealed that training done in a clinical setting comes with a steep learning curve. We also learned that the costs of OT office visits are high and not always covered by insurance.
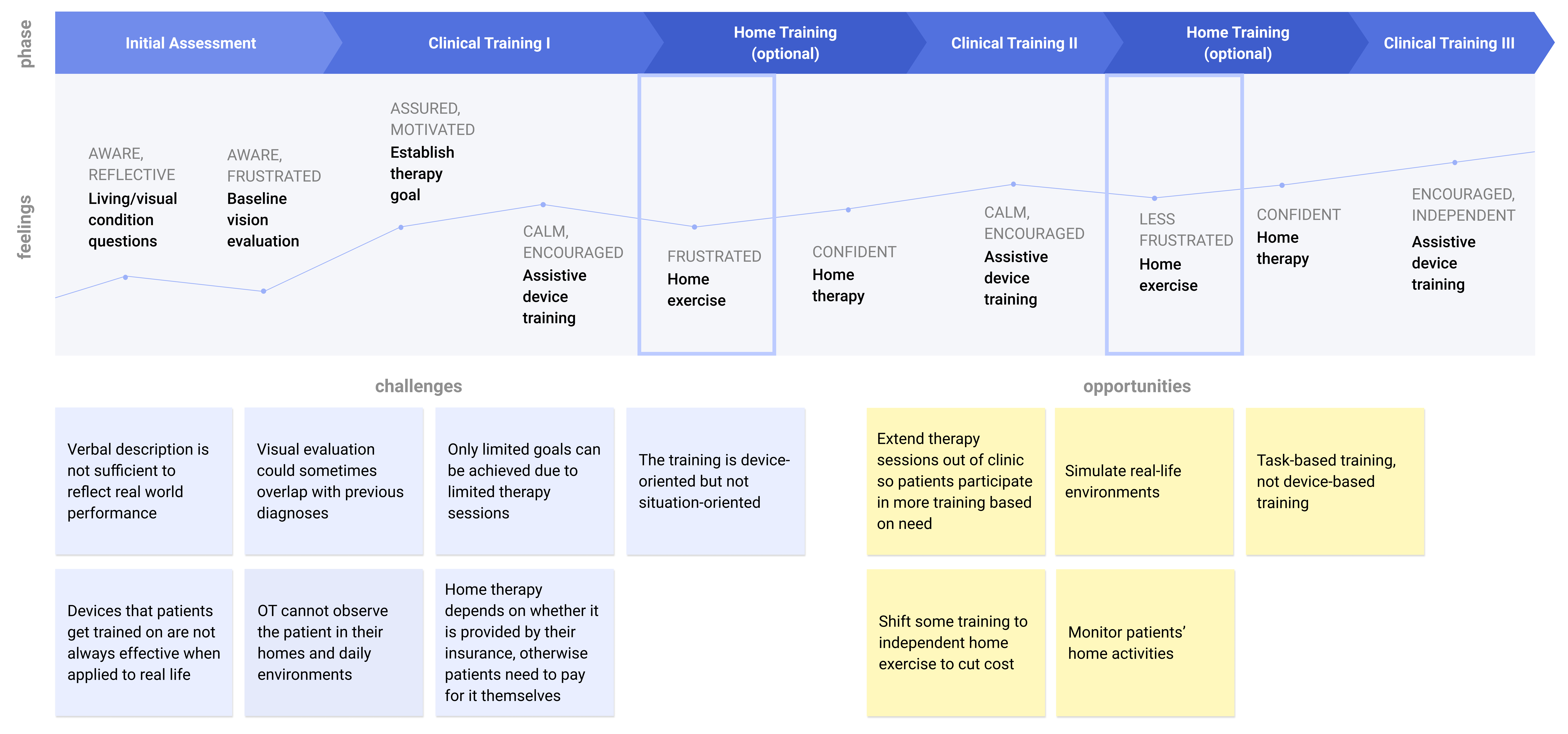
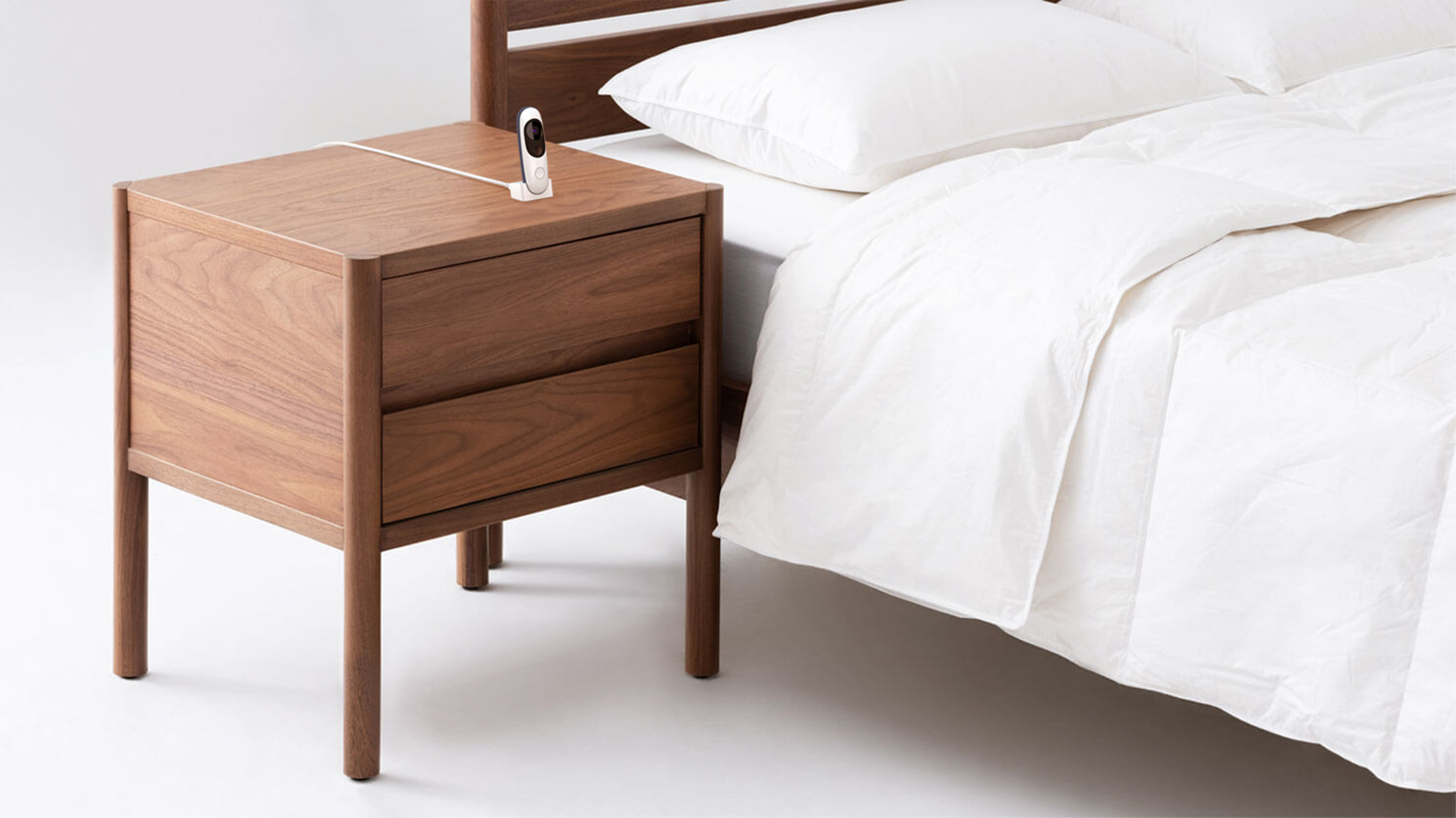
Iris extends the reach of therapy into patients’ homes.
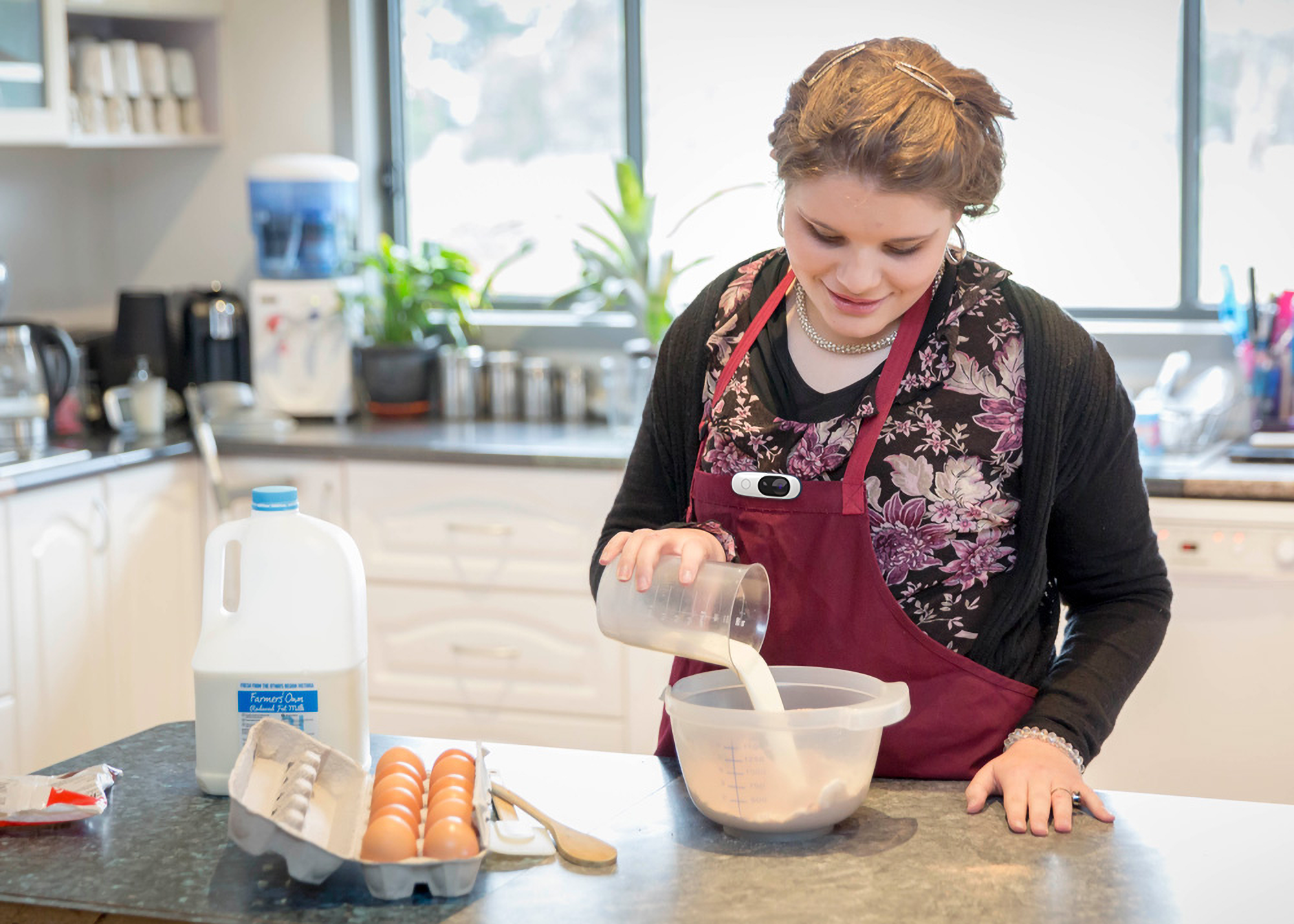

Day in the life
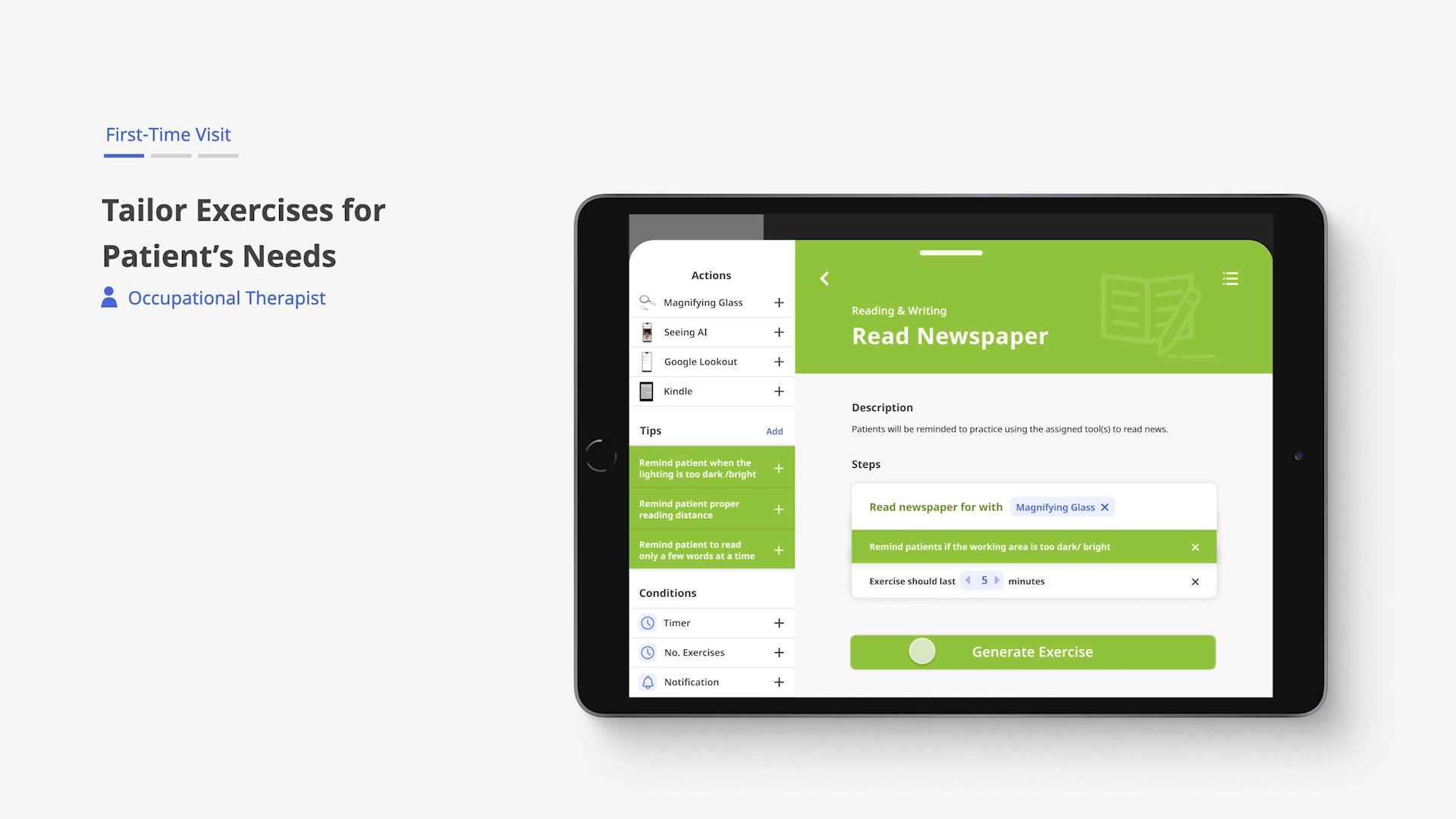
During an OT appointment, therapists use patient goals and diagnoses to create personalized at-home exercises, which are uploaded to the Iris cloud.

At home, patients choose an exercise they want to begin and upload to the Iris wearable tracker.
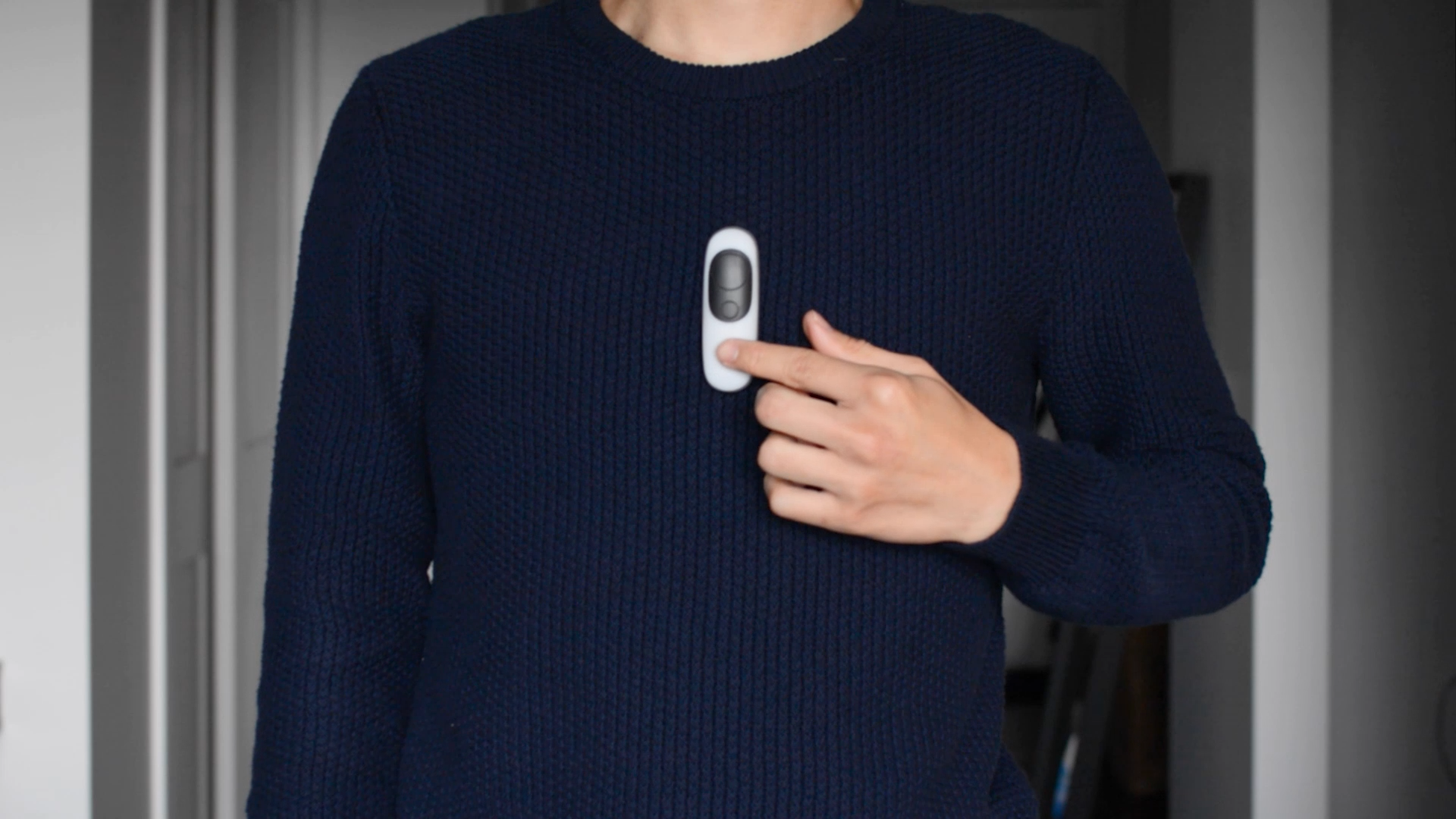

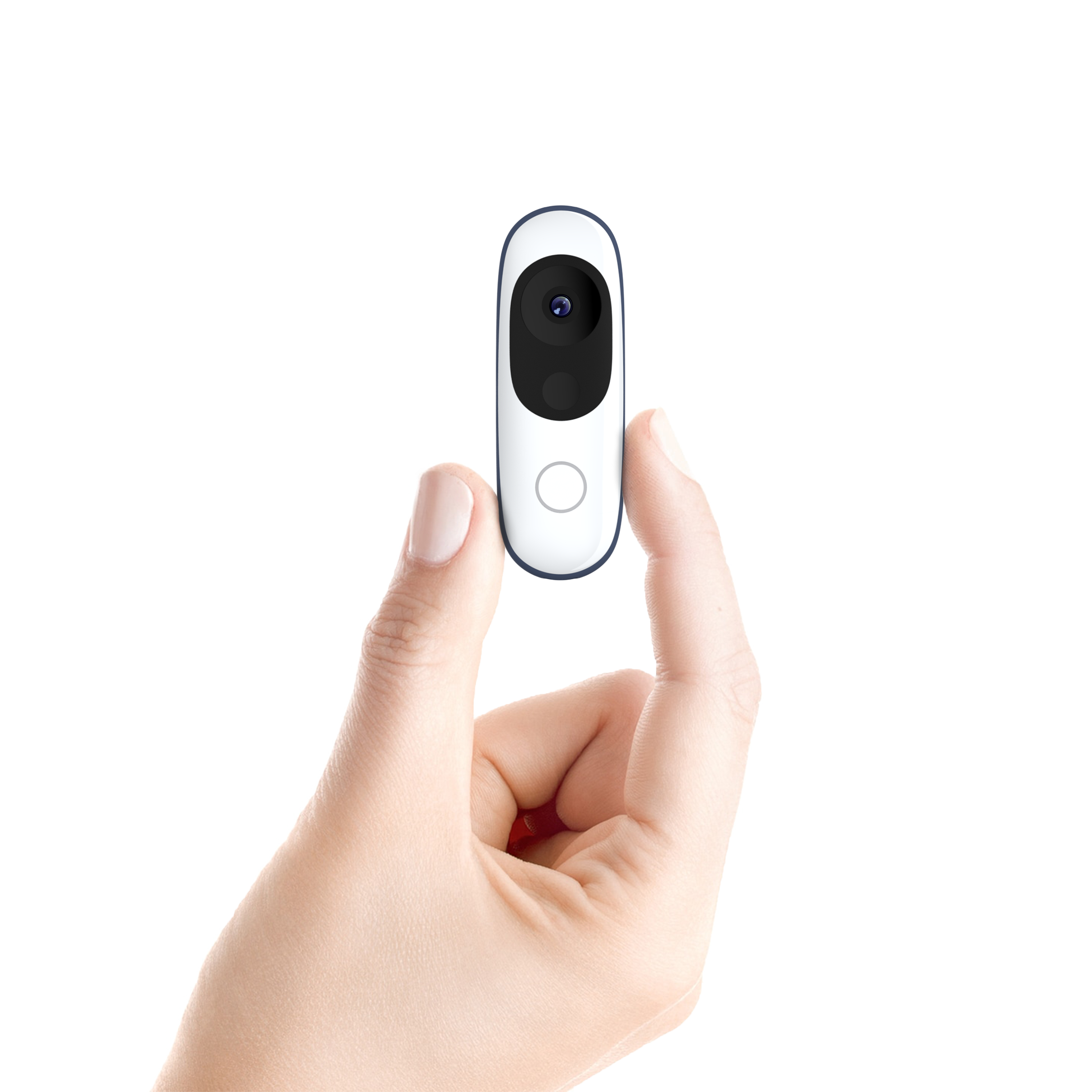
A single button controls the Iris tracker – simply press once to wake Iris and begin the exercise.

Spoken guidance provides instructions for patients. Because Iris tracks tasks in real time, it can also provide feedback and assistance. Tonal cues notify patients of progress throughout sessions.

Once an exercise is completed, Iris summarizes the activity. Video snippets of the session are synced with the app and shared with the occupational therapist.
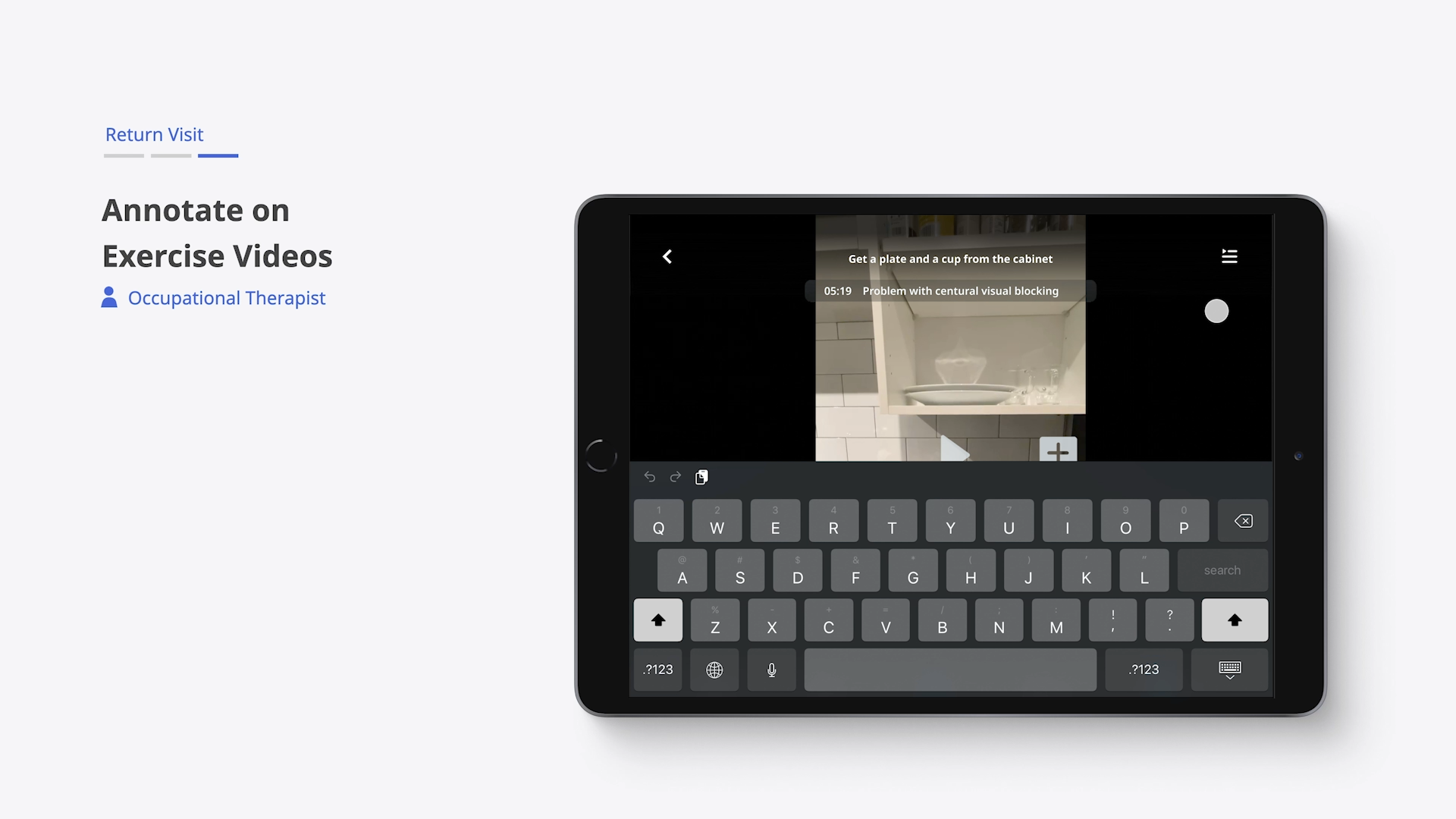
Exercise details are made available for therapists to evaluate in preparation for the next appointment.
Advanced sensing
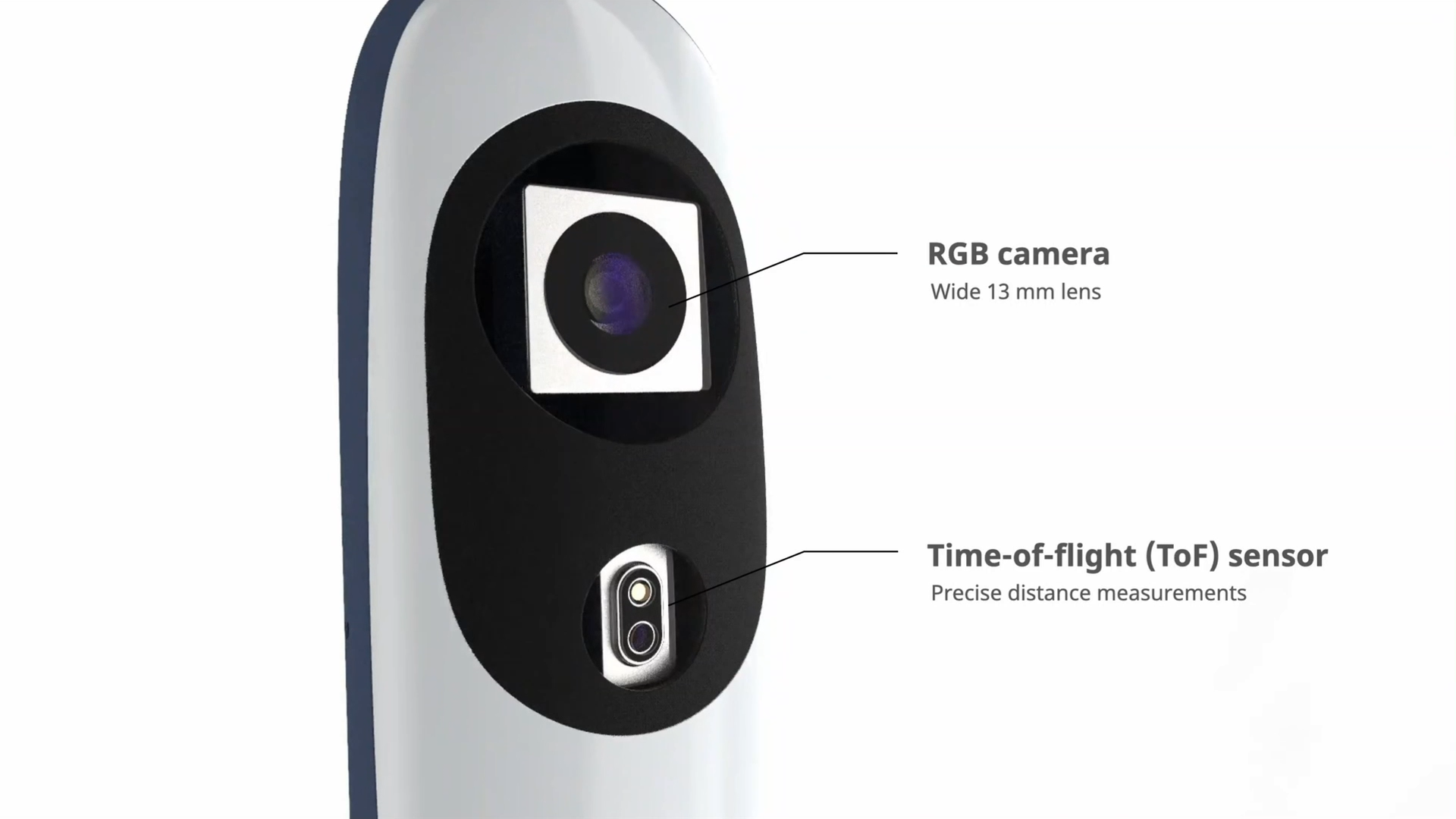

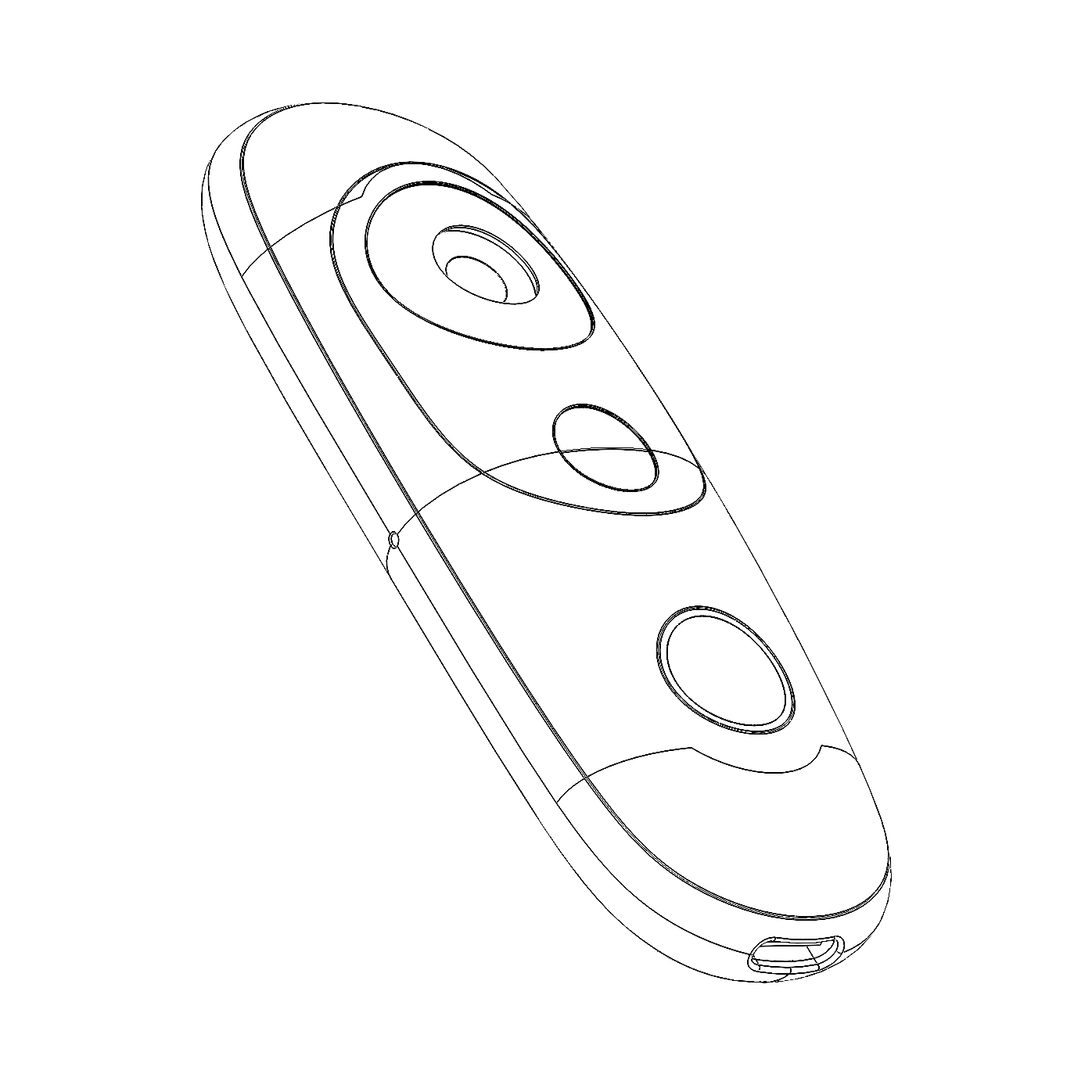
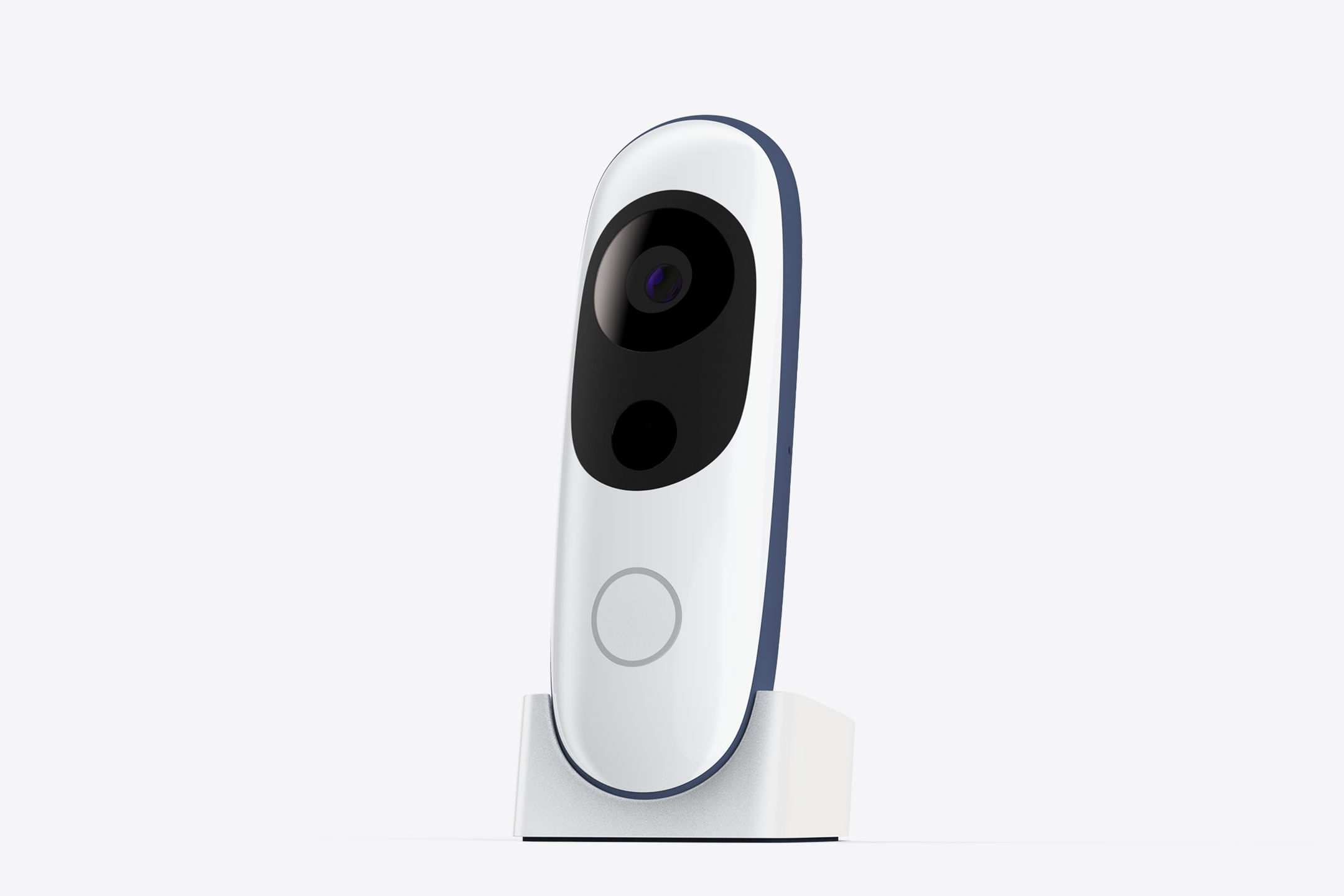
Iris integrates a wide angle camera, a time-of-flight sensor, and a motion-sensing gyroscope. The inputs from these sensors are fed into computer vision algorithms that run completely on-device, enabling Iris to recognize people, objects, and environments.
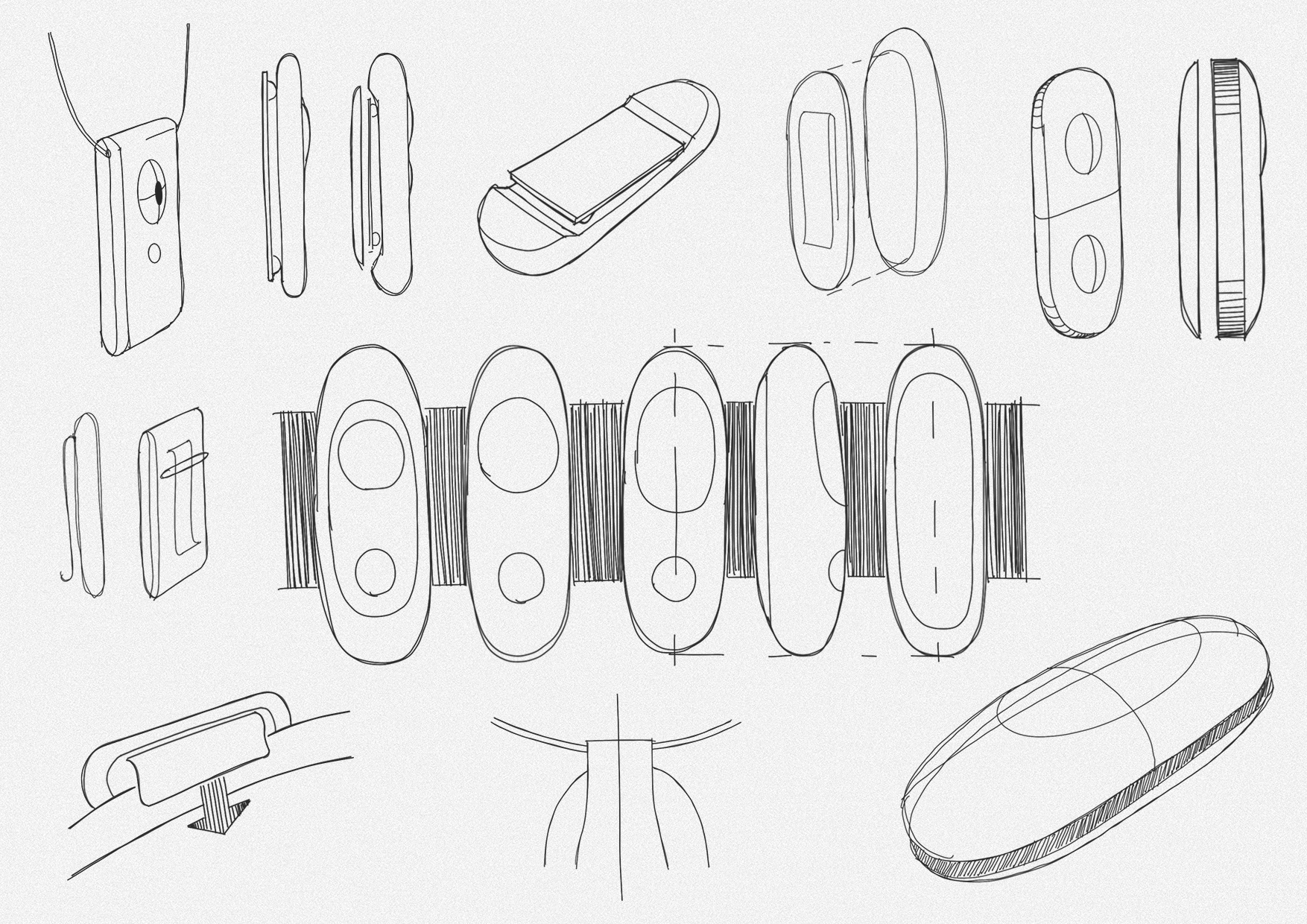
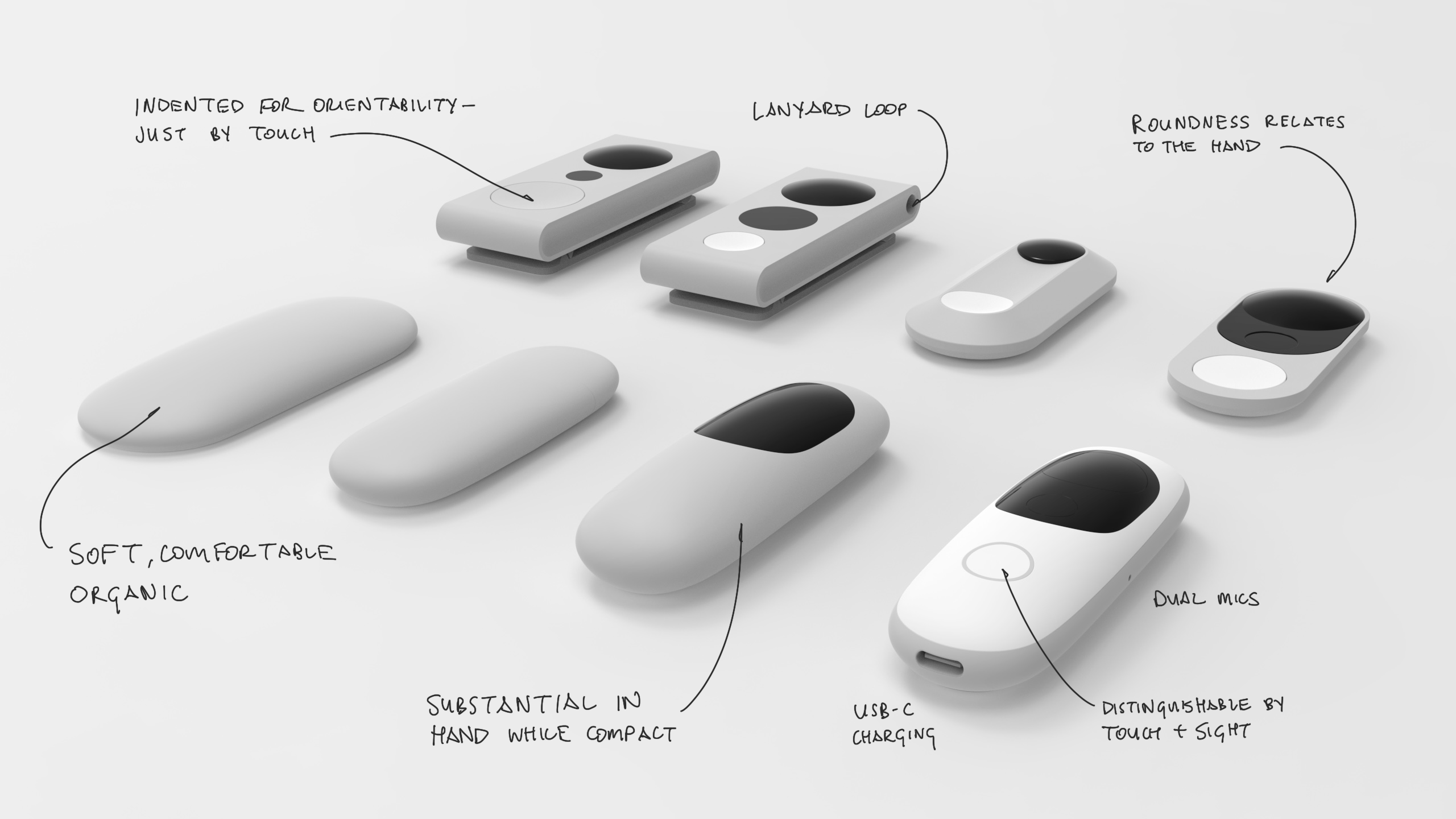
Form development
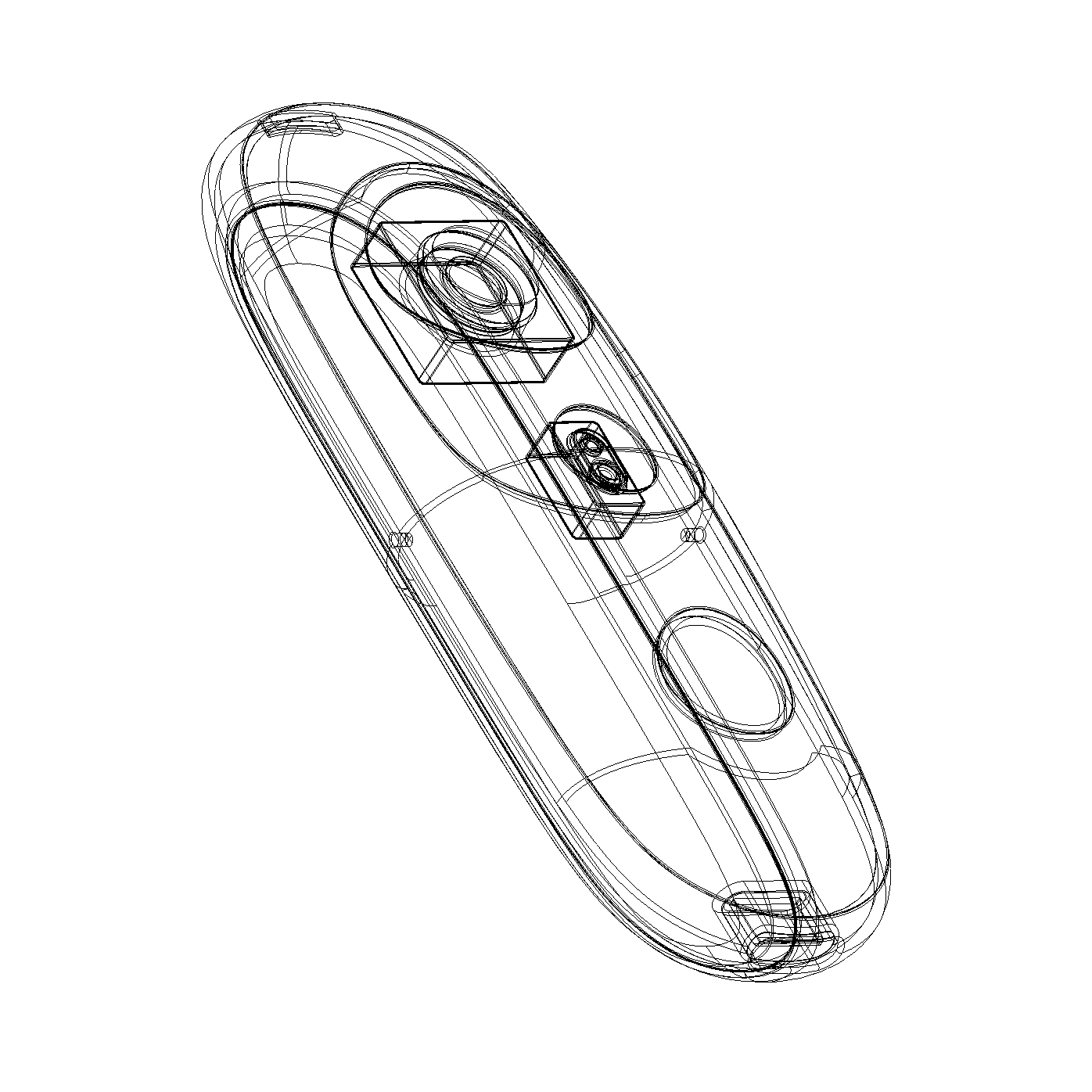
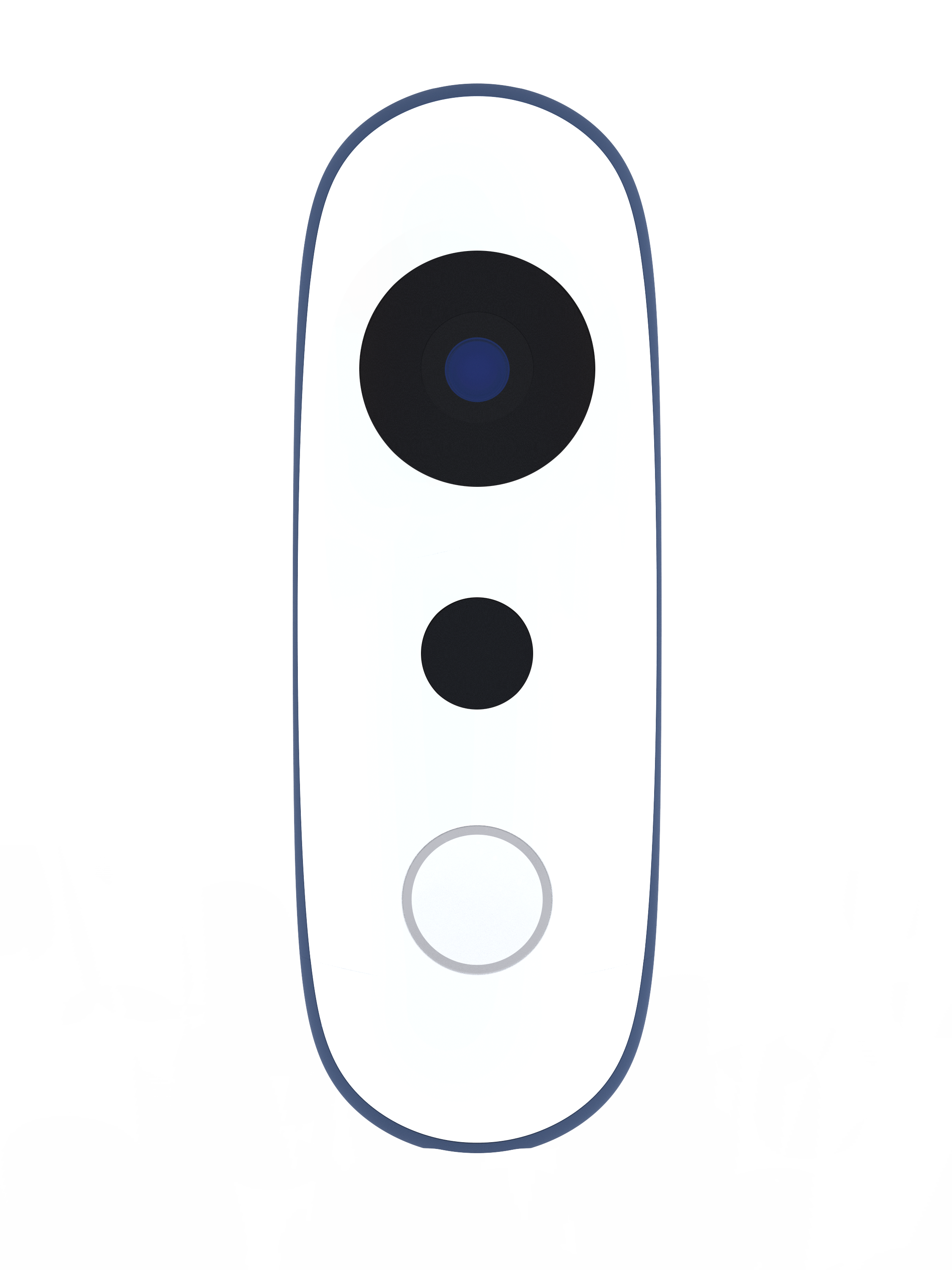

 “It’s a camera”
“It’s a camera”→
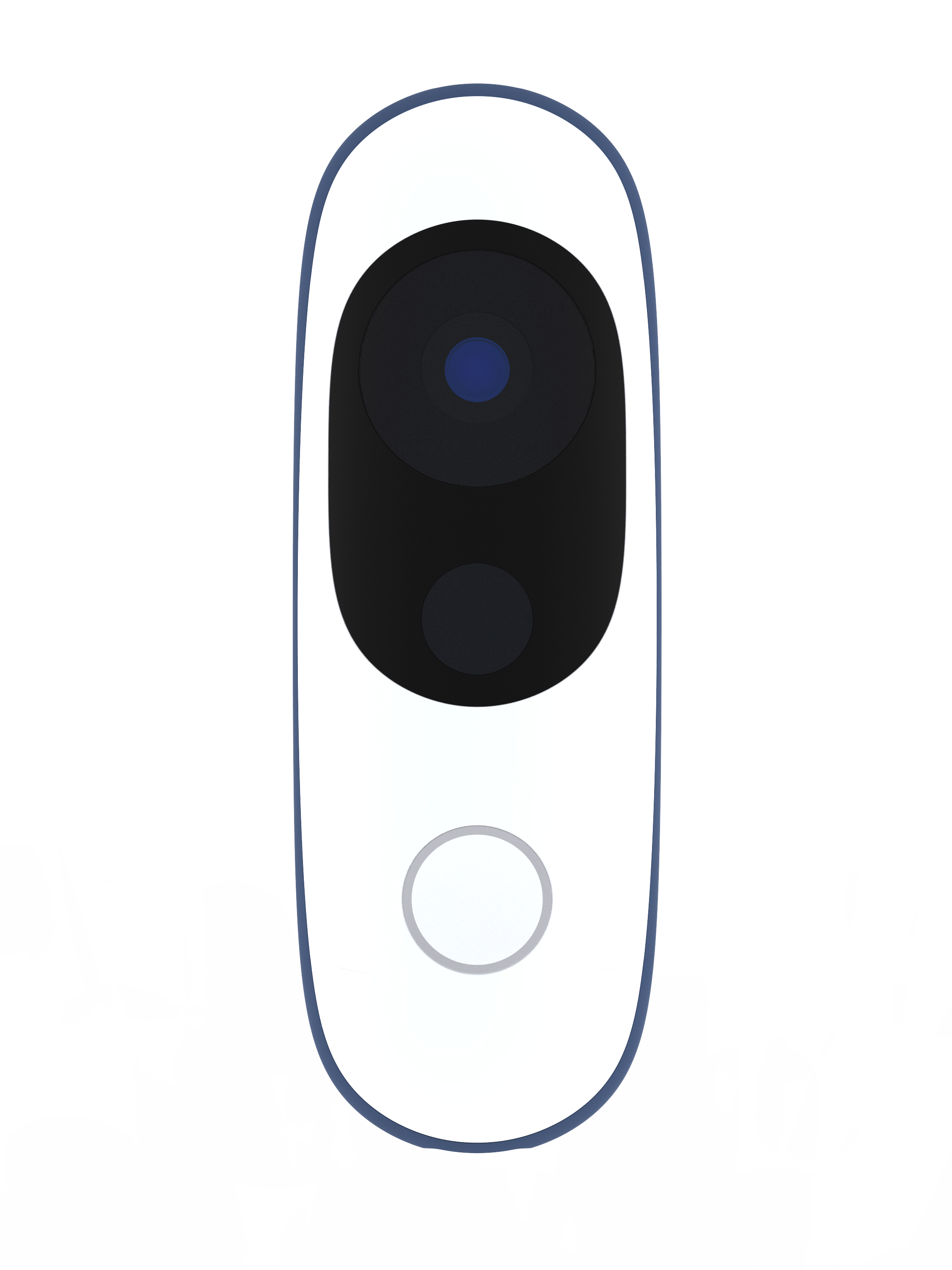

“This is Iris”
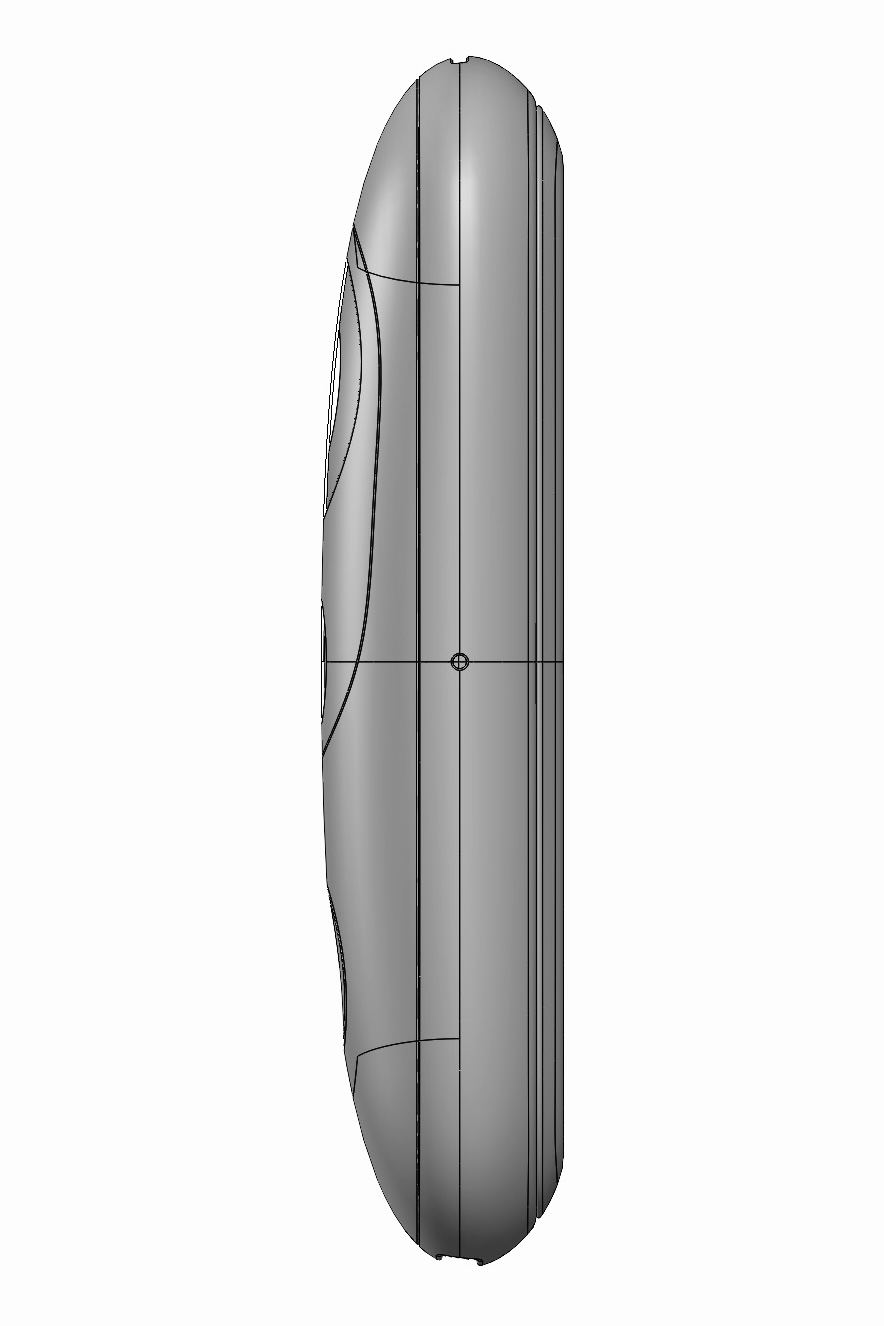
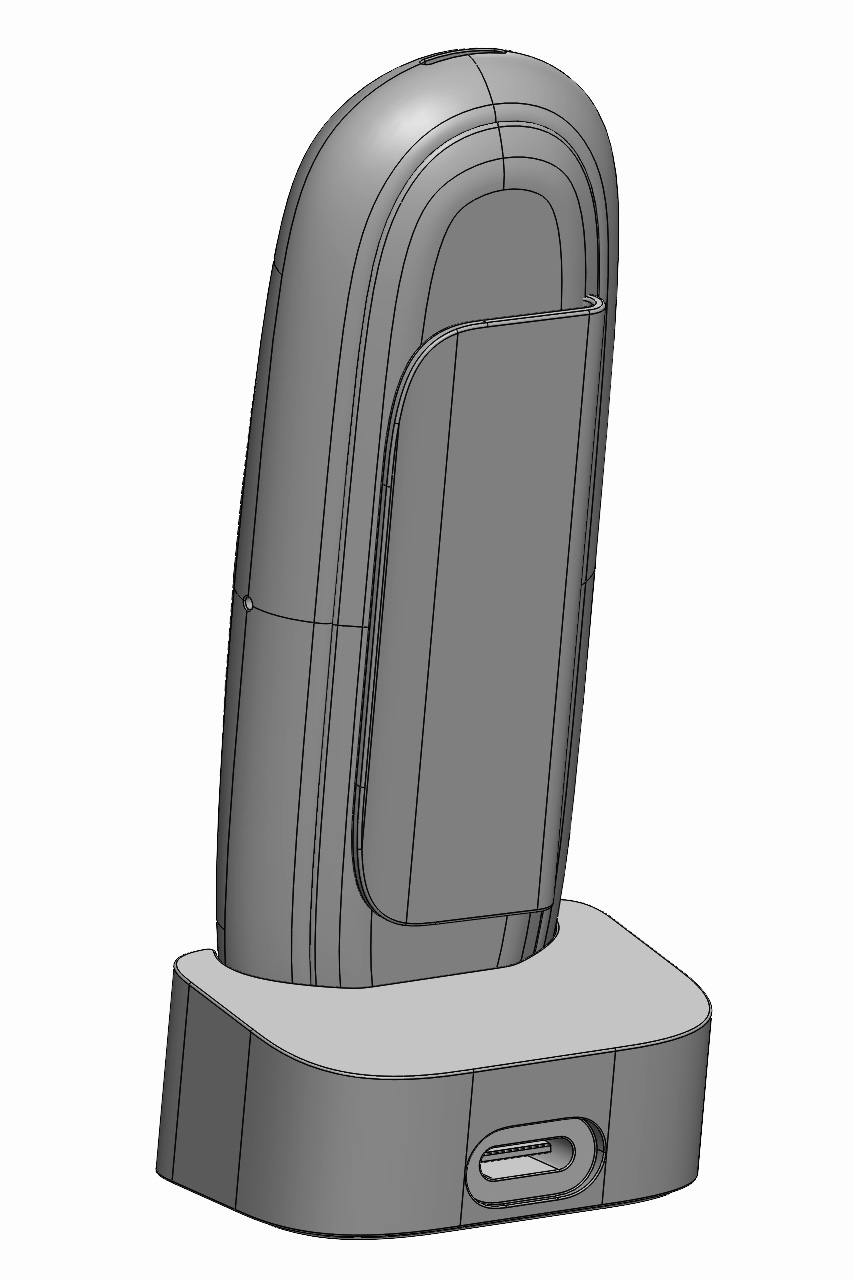
The visor contains the sensing components, harmonizing their lenses with Iris’ enclosure.
The resulting silhouette has a graphic quality that speaks to the deeper functionality within.
The resulting silhouette has a graphic quality that speaks to the deeper functionality within.


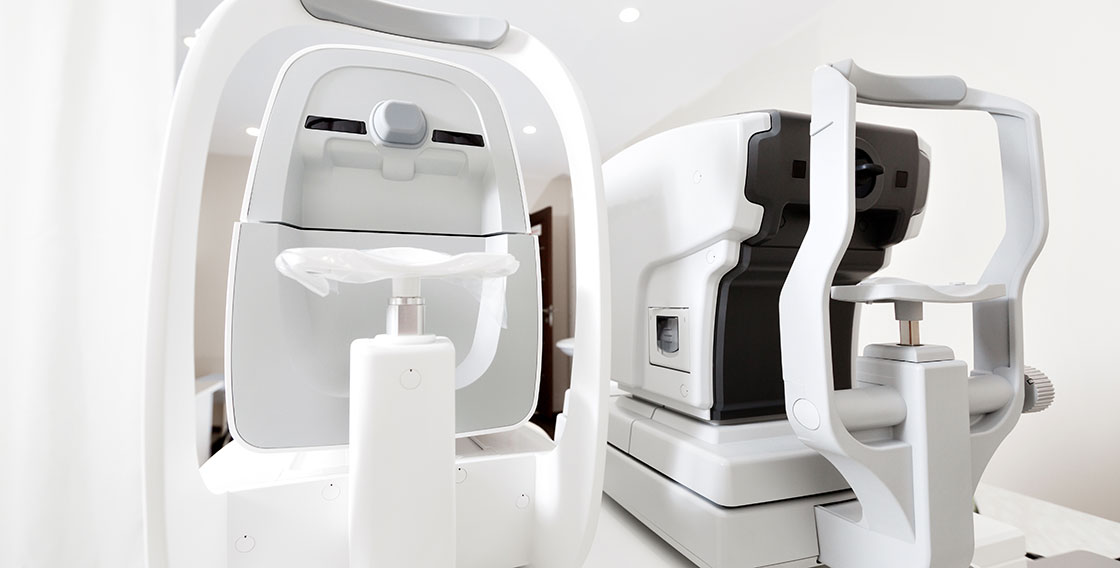
Optometry equipment
![]()
![]()
![]()
Clinical setting
Industrial
Sterile
Patient hands–off
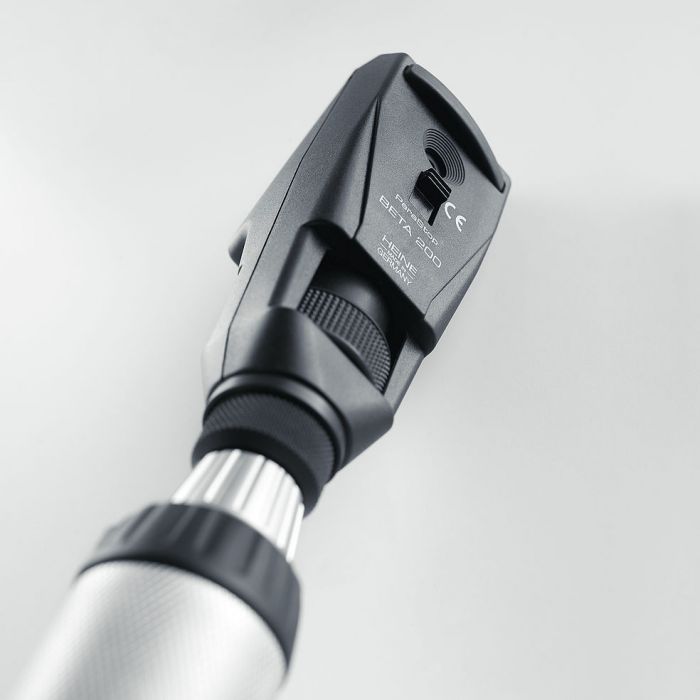


Clinical setting
Industrial
Sterile
Patient hands–off
Iris
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Belongs in the home + hand
Clear touchpoints
Approachable
Graphic
Forward–looking
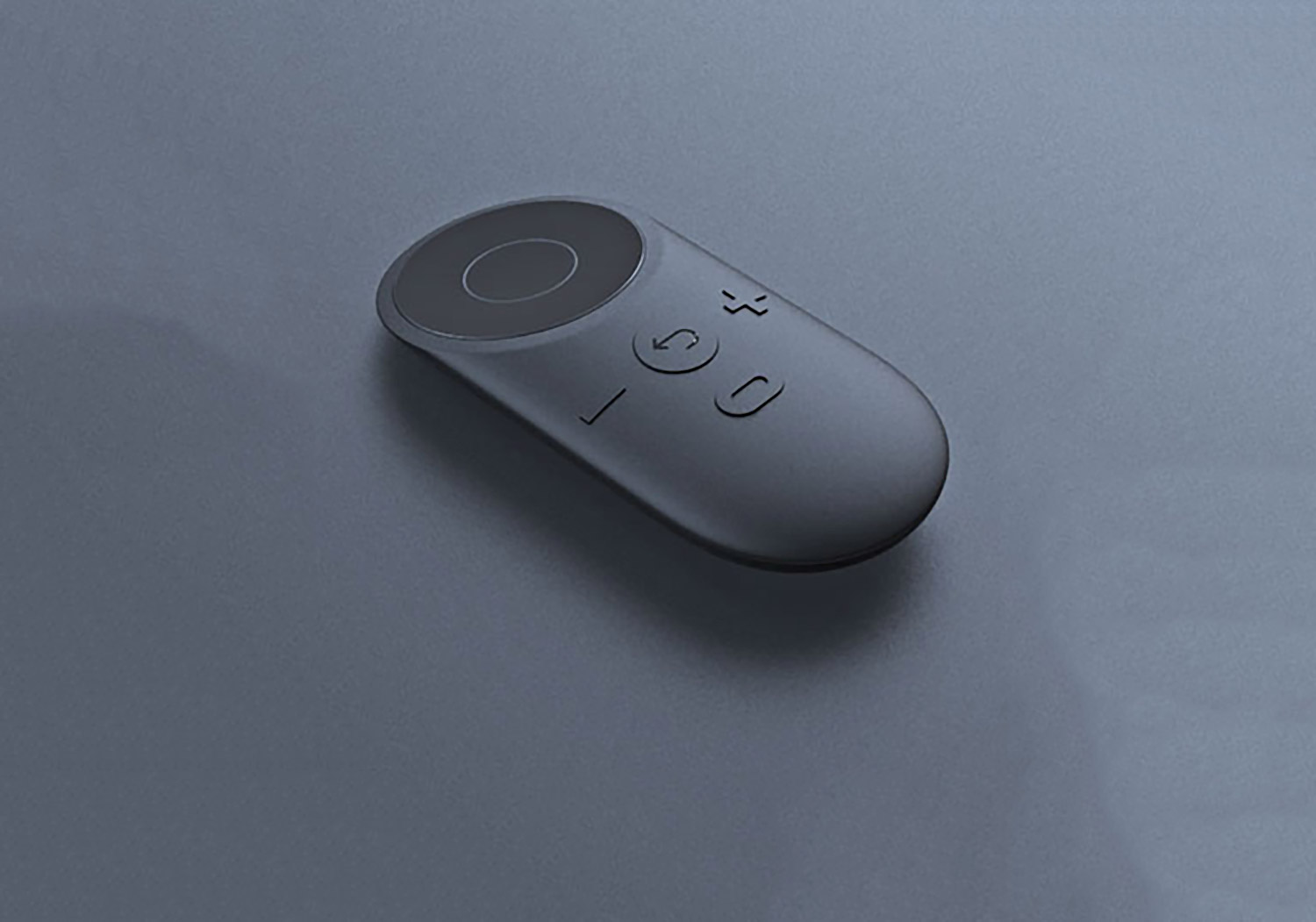





Belongs in the home + hand
Clear touchpoints
Approachable
Graphic
Forward–looking
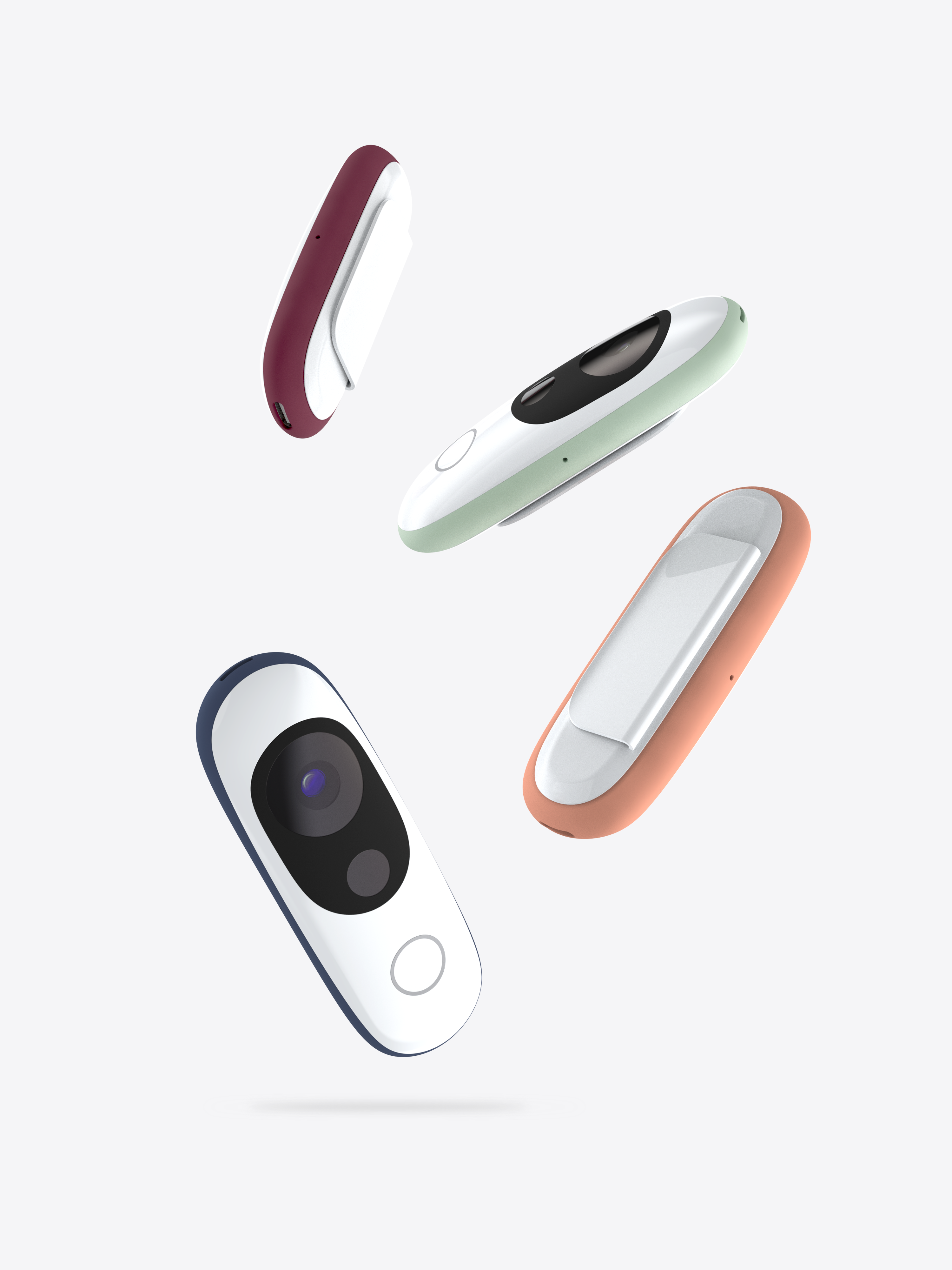




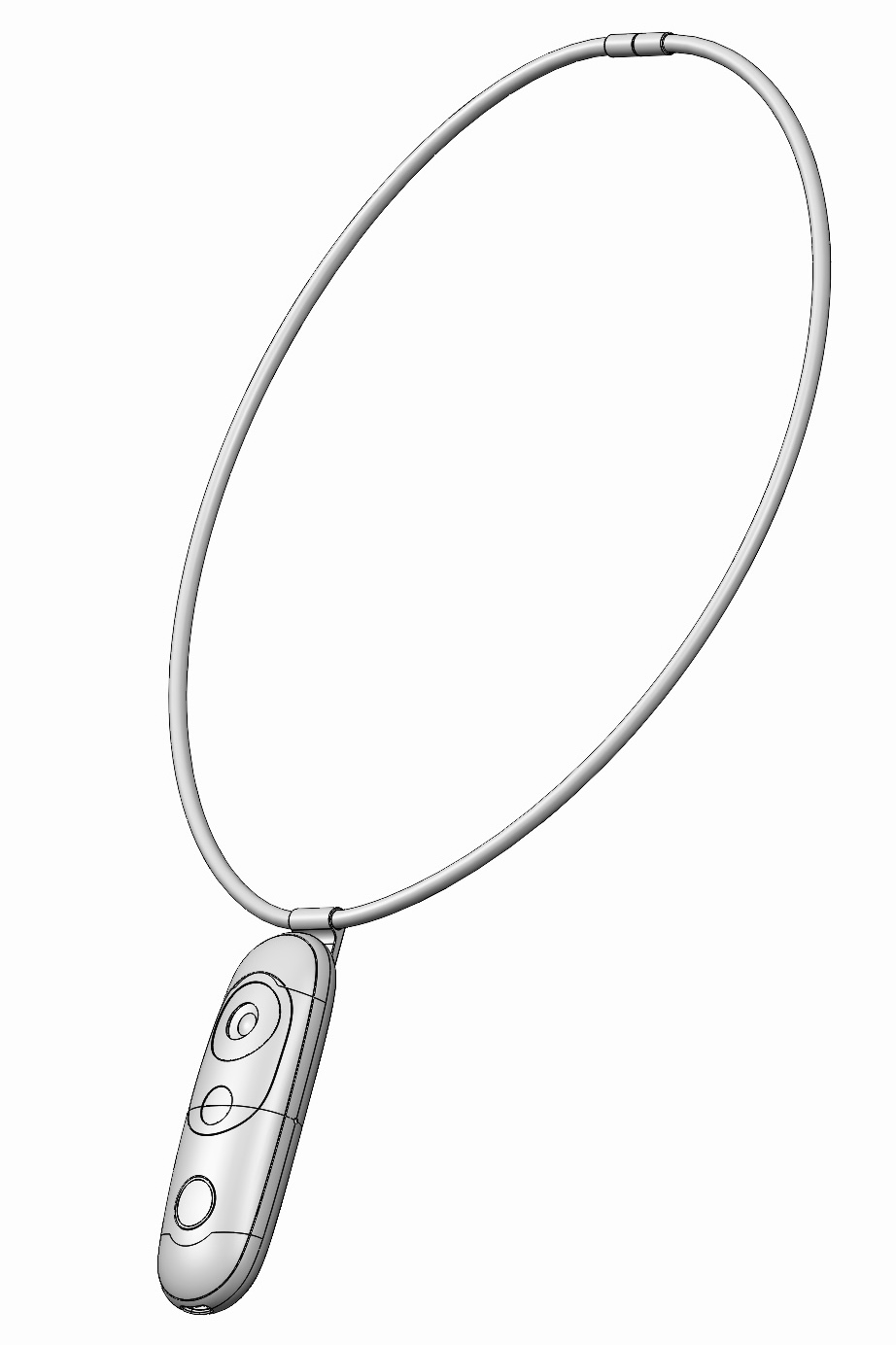
Magnetic backs enable different methods of wearing depending on preference. Swapping between backs is simple and easy.




